Thursday, December 17, 2009
Lookup Cache in Informatica
Lets say we are doing a lookup on the employee table which has - Empno, ename,salary
Now we want to check if the empno is present then update else insert. So we do a lookup on the table
The data resulted from the lookup query will be stored in the cache (index and data cache), each record from the source is looked up against this cache. Now checking against the condition port column is done in the Informatica Lookup cache and not in the database. Due to this any index created in the database has no effect or imporvement on the performance of the lookup.
Can we replicate the same index in Lookup Cache? We don't need to do this. PowerCenter create Index and Data cache for the Lookup. In our case, condition port data - "EMPNO" is indexed and hashed in Index cache and the rest data is found in Data cache.
Now let's consider another lookup case, disable lookup cache. In this kind of Lookup, there is no cache. Everytime a row is sent into lookup, the SQL is executed against database. In this case, the database index may work. But, if the performance of the lookup is a problem, then "cache-less" lookup itself may be a problem.
We should go for cache-less lookup if our source data record is less than the number of records in my lookup table. In this case ONLY, indexing the condition ports will work. Everywhere else, it is just a mere chanse of luck, that makes the database pick up index.
Putting a where condition in the lookup, fetching the minimum required rows in lookup definately adds up to the performance and should always be taken care of.
Happy caching !!
Friday, December 4, 2009
How do you run a full DAC load
If DAC is running incremental everyday and due to some reason you want to do a full load then
You need to reset the Data Warehouse > DAC Client ver 7.9.5. Click on "Tools" --> "ETL Management" --> "Reset Data Warehouse" , it will prompt for
This action will cause all tables that are loaded during
next ETL to be truncated.
Do you want to proceed? >> Yes
This will truncate all the tables, drop indexes and do a full load of dimensions and facts then recreate indexes and compute stats.
What 'Reset Datawareshouse' does is it just updates last_refresh_dt of w_etl_refresh_dt to NULL.
The other way to do it is go to metadata tables and set the Last_refresh_dt to NULL
select row_wid,last_upd,dbconn_wid,ep_wid,table_name,last_refresh_dt,total_count,curr_process_count,version_id from w_etl_refresh_dt
update w_etl_refresh_dt set last_refresh_dt=NULL;
commit;
This will do a full DAC load.
Oracle Tuning
alter system set optimizer_mode=first_rows_10;
alter session set optimizer_goal = all_rows;
select /*+ first_rows(100) */ from student;
We need to start by defining what is the "best" execution plan for a SQL statement. Is the best execution plan the one that begins to return rows the fastest, or is the best execution plan the one that executes with the smallest amount of computing resources? Of course, the answer depends on the processing needs of your database.
The choices of executions plans made by the CBO are only as good as the statistics available to it. The old-fashioned analyze table and dbms_utility methods for generating CBO statistics are obsolete and somewhat dangerous to SQL performance. As we may know, the CBO uses object statistics to choose the best execution plan for all SQL statements.
The dbms_stats utility does a far better job in estimating statistics, especially for large partitioned tables, and the better statistics result in faster SQL execution plans.
Ddbms_stats example that creates histograms on all indexes columns:
BEGIN
dbms_stats.gather_schema_stats(
ownname=>'TPCC',
METHOD_OPT=>'FOR ALL INDEXED COLUMNS SIZE SKEWONLY',
CASCADE=>TRUE,
ESTIMATE_PERCENT=>100);
END;
/
There are several values for the OPTIONS parameter that we need to know about:
GATHER_ reanalyzes the whole schema
GATHER EMPTY_ only analyzes tables that have no existing statistics
GATHER STALE_ only reanalyzes tables with more than 10 percent modifications (inserts, updates, deletes)
GATHER AUTO_ will reanalyze objects that currently have no statistics and objects with stale statistics. Using GATHER AUTO is like combining GATHER STALE and GATHER EMPTY.
Note that both GATHER STALE and GATHER AUTO require monitoring. If you issue the ALTER TABLE XXX MONITORING command, Oracle tracks changed tables with the dba_tab_modifications view.
SQL> desc dba_tab_modifications;
Automating sample size with dbms_stats.The better the quality of the statistics, the better the job that the CBO will do when determining your execution plans. Unfortunately, doing a complete analysis on a large database could take days, and most shops must sample your database to get CBO statistics. The goal is to take a large enough sample of the database to provide top-quality data for the CBO.
According to the Oracle documentation, the I/O and CPU costs are evaluated as follows:
Cost = (#SRds * sreadtim +
#MRds * mreadtim +
#CPUCycles / cpuspeed ) / sreadtim
where:
#SRDs - number of single block reads
#MRDs - number of multi block reads
#CPUCycles - number of CPU Cycles *)
sreadtim - single block read time
mreadtim - multi block read time
cpuspeed - CPU cycles per second
Note that the costs are a function of the number of reads and the relative read times, plus the CPU cost estimate for the query. Also note the external costing does not consider the number of data blocks that reside in the RAM data buffers, but a future release of the optimizer is likely to consider this factor.
Here we see that Oracle uses the both the CPU and I/O cost estimations in evaluating the execution plans. This equation becomes even more complex when we factor-in parallel query where many concurrent processes are servicing the query.
The best benefit for using CPU costing is for all_rows execution plans where costs is more important than with first_rows optimization.
v$sql_plan view can help us locate SQL tuning opportunities
The EXPLAIN PLAN statement displays execution plans chosen by the Oracle optimizer for SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE statements. A statement's execution plan is the sequence of operations Oracle performs to execute the statement.
You can specify a statement Id when using the INTO clause.
EXPLAIN PLAN
INTO my_plan_table
SET STATEMENT_ID = 'bad1' FOR
SELECT last_name FROM employees;
SELECT lpad(' ',level-1)||operation||' '||options||' '||
object_name "Plan"
FROM plan_table
CONNECT BY prior id = parent_id
AND prior statement_id = statement_id
START WITH id = 0 AND statement_id = '&1'
ORDER BY id;
CREATE TABLE emp_range
PARTITION BY RANGE(hire_date)
(
PARTITION emp_p1 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1991','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p2 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1993','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p3 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1995','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p4 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1997','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p5 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1999','DD-MON-YYYY'))
) AS SELECT * FROM employees;
For the first example, consider the following statement:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM emp_range;
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM emp_range
WHERE hire_date >= TO_DATE('1-JAN-1995','DD-MON-YYYY');
CREATE TABLE emp_comp PARTITION BY RANGE(hire_date) SUBPARTITION BY
HASH(department_id)
SUBPARTITIONS 3
(
PARTITION emp_p1 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1991','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p2 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1993','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p3 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1995','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p4 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1997','DD-MON-YYYY')),
PARTITION emp_p5 VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE('1-JAN-1999','DD-MON-YYYY'))
) AS SELECT * FROM employees;
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM emp_comp
WHERE hire_date = TO_DATE('15-FEB-1997', 'DD-MON-YYYY');
How to obtain explain plans
Explain plan for
Main advantage is that it does not actually run the query - just parses the sql. This means that it executes quickly. In the early stages of tuning explain plan gives you an idea of the potential performance of your query without actually running it. You can then make a judgement as to any modifications you may choose to make.
Autotrace
Autotrace can be configured to run the sql & gives a plan and statistics afterwards or just give you an explain plan without executing the query.
Tkprof
Analyzes trace file
Using Oracle hints can be very complicated and Oracle developers only use hints as a last resort, preferring to alter the statistics to change the execution plan. Oracle contains more than 124 hints, and many of them are not found in the Oracle documentation
Optimizer hint is an optimizer directive placed inside comments inside your SQL statement and used in those rare cases where the optimizer makes an incorrect decision about the execution plan. Because hints are inside comments, it is important to ensure that the hint name is spelled correctly and that the hint is appropriate to the query.
Oracle Hints
SELECT /*+ hint --or-- text */ statement body
Thursday, December 3, 2009
Oracle Table Lock
select
c.owner,
c.object_name,
c.object_type,
b.sid,
b.serial#,
b.status,
b.osuser,
b.machine
from
v$locked_object a ,
v$session b,
dba_objects c
where
b.sid = a.session_id
and
a.object_id = c.object_id;
Do the following >>
select object_id from dba_objects where object_name='tablename';
select * from v$locked_object where object_id=id number;
Note the "oracle_username" and "session_id".
Or you can query v$access
select sid from v$access where owner='table owner' and object='table
name';
Note the session id number or "sid".
select sid, serial#, command, taddr from v$session where sid=session id
number;
Now you have identified the user and what they are doing.
To terminate the session:
Alter system kill session 'sid, serial#' immediate;
The session should now be killed and the lock SHOULD release.
Rechecking "v$locked_object" will tell you this. If the lock does not
immediately release, there may be a rollback occuring.
To check for rollback:
select used_ublk from v$transaction where ADDR=value from TADDR in
v$session;
select c.owner, c.object_name, c.object_type,b.sid, b.serial#, b.status, b.osuser, b.machine
from v$locked_object a , v$session b, dba_objects c
where b.sid = a.session_id
and a.object_id = c.object_id;
select
username,
v$lock.sid,
trunc(id1/power(2,16)) rbs,
bitand(id1,to_number('ffff','xxxx'))+0 slot,
id2 seq,
lmode,
request
from v$lock, v$session
where v$lock.type = 'TX'
and v$lock.sid = v$session.sid
and v$session.username = USER
Informatica Metadata
The widget refers to the types of transformation details stored in these tables.
Widget Ids and transformation types
widget_type Type of transformation
1 Source
2 Target
3 Source Qualifier
4 Update Strategy
5 expression
6 Stored Procedures
7 Sequence Generator
8 External Procedures
9 Aggregator
10 Filter
11 Lookup
12 Joiner
14 Normalizer
15 Router
26 Rank
44 mapplet
46 mapplet input
47 mapplet output
55 XML source Qualifier
80 Sorter
97 Custom Transformation
select z.widget_id, decode(z.porttype, 1, 'INPUT', 3, 'IN-OUT', 2, 'OUT', 32, 'VARIABLE', 8, 'LOOKUP', 10, 'OUT-LOOKUP', to_char(z.porttype)) Port_Type from opb_widget_field z;
If you want to know the mapping name, then match the widget_id against the widget_id of opb_widget_inst and then pull the mapping_id which can be mapped against mapping_id in opb_mappings table. If you want to know the Folder name, then map the subject_id from opb_mappings to that of subj_id in OPB_SUBJECTS table to get the subject_name.
OPB_EXPRESSION is the table that stores all the expressions in metadata. To associate an expression to a field in a transformation, OPB_WIDG_EXPR is the table to be used.
select g.expression from opb_widget_expr f, opb_expression g where f.expr_id = g.expr_id;
SQL overrides can be in Source Qualifiers and Lookup transformations.
To get the SQL Override from metadata, check REP_WIDGET_ATTR.ATTR_VALUE column.
select * from opb_widget_field where wgt_datatype=11
select g.expression from opb_widget_expr f, opb_expression g where f.expr_id = g.expr_id;
select * from REP_WIDGET_ATTR
select * from opb_mapping -- to check for mapping,mapplet, its stauts of valid/invalid etc
select * from opb_server_info -- to get server hostname,ip,etc
select src_id from opb_src where source_name ='W_DAY_D' -- source table , owner info
select * from opb_src_fld where src_id=1753 -- to get table column/field list info
select * from opb_targ where target_name like 'W_DAY_D' -- target table info
select * from opb_targ_fld where target_id =1835 -- to get target field info
Friday, November 13, 2009
Data Warehouse Concepts - Part 2
In data modeling following tasks are performed in an iterative manner:
• Identify entity types
• Identify attributes
• Apply naming conventions
• Identify relationships
• Apply data model patterns
• Assign keys
• Normalize to reduce data redundancy (Entity Relationship Model)
• Denormalize to improve performance (Dimensional Model)
· Logical modeling
· Physical modeling
Logical modeling deals with gathering business requirements and converting those requirements into a model. The logical model revolves around the needs of the business, not the database, although the needs of the business are used to establish the needs of the database. Logical modeling involves gathering information about business processes, business entities (categories of data), and organizational units. After this information is gathered, diagrams and reports are produced including entity relationship diagrams, business process diagrams, and eventually process flow diagrams. The diagrams produced should show the processes and data that exists, as well as the relationships between business processes and data. Logical modeling should accurately render a visual representation of the activities and data relevant to a particular business.
Typical deliverables of logical modeling include
Entity relationship diagrams :
Business process diagrams :
User feedback documentation :
Physical modeling involves the actual design of a database according to the requirements that were established during logical modeling. Logical modeling mainly involves gathering the requirements of the business, with the latter part of logical modeling directed toward the goals and requirements of the database. Physical modeling deals with the conversion of the logical, or business model, into a relational database model. When physical modeling occurs, objects are being defined at the schema level. A schema is a group of related objects in a database. A database design effort is normally associated with one schema.
During physical modeling, objects such as tables and columns are created based on entities and attributes that were defined during logical modeling. Constraints are also defined, including primary keys, foreign keys, other unique keys, and check constraints. Views can be created from database tables to summarize data or to simply provide the user with another perspective of certain data. Other objects such as indexes and snapshots can also be defined during physical modeling. Physical modeling is when all the pieces come together to complete the process of defining a database for a business.
Physical modeling is database software specific, meaning that the objects defined during physical modeling can vary depending on the relational database software being used. For example, most relational database systems have variations with the way data types are represented and the way data is stored, although basic data types are conceptually the same among different implementations. Additionally, some database systems have objects that are not available in other database systems.
Typical deliverables of physical modeling include the following:
Server model diagrams:
User feedback documentation :
Designing the Data warehouse
Main emphasis in the design is on fast query retrieval rather than transactional performance. The design should be such that it enables analysis of data from any angle at any given point of time.
Dimensional Data Model is the best way of designing a data ware house. The main terms used in dimensional modeling are facts and dimensions.
1. Fact - A fact is a single iteration in a historical record
2. Dimension - A dimension is something used to dig into, divide, and collate those facts into something useful
Facts represent historical or archived data and dimensions represent smaller static data entities. It follows that dimension entities will generally be small and fact entities can become frighteningly huge. Fact entities will always be appended to, and dimension entities can be changed, preferably not as often as the fact entities are appended to. The result is many very small entities related to data in groups from very large entities.
Granularity
While designing a fact the most important point to keep in mind is the granularity, how much data to keep and to what level of detail. So do we need to store all transaction or do we store it at summary level. Like in case of a Retailer and Manufacturer, a Retailer would like to capture each and every piece of an item sold from its point of sale i.e. at the lowest Stock keeping unit level to maintain its inventory better, where as the Manufacturer might keep it at a level higher than the pieces, they would not need information of each piece sold, they might be interested to keep record at an Item level, one level above Stock keeping as compared to Retailers. So depending on business needs we need to decide the lowest possible granular level to be kept in facts to make the reporting accurate. From a planning perspective, it might be best to begin by retaining all facts down to the smallest detail if at all possible. Data warehouses are expected to be large, and disk space is cheap.
Star and Snow Flake Schema
A star schema contains one, or at least very few, very large fact entities, plus a large number of small dimensional entities. As already stated, effectively fact entities contain transactional histories and dimension entities contain static data describing the fact entity archive entries. The objective for performance is to obtain joins on a single join level, where one fact entity is joined to multiple small dimension entities, or perhaps even a single dimension entity.
A snowflake schema is a normalized star schema such that dimension entities are normalized.
A single data warehouse can contain multiple fact entities and, therefore, multiple star schemas. Additionally, individual dimension entities can point to multiple fact entities. Dimension entities will occupy a small fraction of the storage space than fact entities do. Fact entities in a data warehouse can have trillions of rows, whereas dimensions are in the range of tens, hundreds or perhaps thousands. Any larger than thousands and those dimensions could possibly be facts.
Tuesday, November 10, 2009
Data Warehouse Concepts : Part 1
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a relational database that is designed for query and analysis rather than for transaction processing. It usually contains historical data derived from transaction data, but can include data from other sources like EBS, SAP, Siebel, apart from your existing OLTP system in use. Data warehouses is mainly used for analysis and is separate from transaction workload, it enables an organization to consolidate data from several sources to come up for a centralized place where analysis can be done faster and in a better way. This helps in:
1. Maintaining historical data
2. Analyzing the data to gain a better understanding of the business and to improve the existing business.
In addition to a relational database, a data warehouse environment can include an extraction, transportation, transformation, and loading (ETL) solution (depending on the type/tool it can be ETL,ELT or ETL solutions), statistical analysis, reporting, data mining , client analysis , and many other applications that manage the process of gathering data, transforming it into useful information and finally delivering it to business users.
Why is it different from the existing Transaction system - OLTP or transactional database is mainly used for the purpose of daily activity i.e. Insert/update/delete i.e. to store data for daily operational purpose. Data warehouse or OLAP system is on top of this - ie it takes data from OLTP and transforms it for the management to come up with analysis on it, reporting, ad hoc reports so that better decisions can be made, where as end user of an OLTP system is the Operational team who maintains the day to day activities of the business.
Lets take for example a railway ticket booking system - when I enter in irctc.co.in to book my ticket then the main purpose is to get a seat booked – Operational. For this the backend data model/tables/ physical objects have to be designed in such a way that it helps in easy and fast processing of Inert/Update and Deleting of data. The best way of doing this is to have a Normalized database model which is the OLTP system (On line transaction processing) which stores data in the 3NF form making the data transfer very fast. Now when I enter my information it goes at the back end in numerous tables which are in the 3NF form enabling my processing faster for a ticket booking, same is the case of ATM transaction, shopping anything related to Operational Data i.e. day to day transactions. After I have booked my ticket, my work is done. The railway helpdesk maintaining this – his work is done. We have a vast database which maintains daily data.
After this lets talk on the other side of the Railway department – the ministry now wants to come up with which routes are doing good, which are less profit making, which services are running in profit and where there a need for improvement. Lets take for example, the management wants reports like –
a. Most profit making route in terms of day/train/passenger wise
b. Least profit making route in terms of day/train/passenger wise
c. Monthly report on same line
d. Quarterly report on same line
e. Yearly report on same line
f. Comparison of this day to same day in history, this month to same month last year, this quarter to last quarter, to last year etc.
g. Comparison of two routes in terms of profit, maintenances , time lines
There can be numerous reports that the management might want to look at for analysis and decision making at any given point of time. There can be a need of ad hoc reports also which might be required for some important presentations, decisions.
For all of this to happen, imagine a team of reporting people struggling hard to make different joins, different source data, consolidating data, cleansing operational data, integrating them, making them as per the required subject areas on top of huge and vast set of tables, a network of tables which are in the 3NF form making it a non user friendly environment for understanding and working on. Even if there is an expert in Oracle lets say, but data is coming from Oracle, Teradata, db2 and sap for different lines, different regions. Employee data is in different source, different format, trains information is in different format. Imagine the amount of work required to consolidate this information and come up with joins etc to make simple reports. It will take years to implement this reporting requirement on an OLTP system and an expert team of each area. More work, more people, more time required at each level making it a very difficult and cumbersome job that too question to reliability and stability. How to get historical data from archive files, how to centralize data from different places, how to make meaning to all the tables
Now imagine a data warehouse on top of this - a denormalized model which will help in maintaining the historical data from different sources at a centralized place to make the reporting a very easy job. Lets take the OLTP data and on top of that build our data warehouse model – we can have a Star, Snow flake schema, or a hybrid schema to facilitate this. We will need to come up with a Logical data model and then Physical data model. All this will be done to come up with a model that will help in storing data in such a way that it is easily retrievable and gives fast report building and query execution state to make it the best way of reporting for the management which in turn can come up with better decision making for any organization.
So coming back to our example of Railway system – what all do we need. First is requirement gathering , assume completed. Then to make a data warehouse we need to consider its characteristic like –
1. Subject Oriented
2. Integrated
3. NonVolatile
4. Time Variant
Data Warehouse Architectures
Now that we have decided to have a data warehouse, we need to decide how our architecture will be out of the commonly used three forms
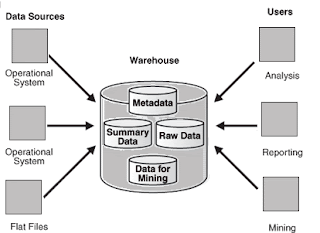
1. Basic – End users directly access data derived from several source systems through the data warehouse
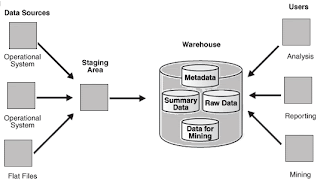
2. With Staging Area – We need to clean and process our operational data before putting it into the warehouse. A staging area simplifies building summaries and general warehouse management
Saturday, November 7, 2009
PERT
Complex projects require a series of activities, some of which must be performed sequentially and others that can be performed in parallel with other activities. This collection of series and parallel tasks can be modeled as a network.
In 1957 the Critical Path Method (CPM) was developed as a network model for project management. CPM is a deterministic method that uses a fixed time estimate for each activity. While CPM is easy to understand and use, it does not consider the time variations that can have a great impact on the completion time of a complex project.
The Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a network model that allows for randomness in activity completion times. PERT was developed in the late 1950's for the U.S. Navy's Polaris project having thousands of contractors. It has the potential to reduce both the time and cost required to complete a project.
The Network Diagram
In a project, an activity is a task that must be performed and an event is a milestone marking the completion of one or more activities. Before an activity can begin, all of its predecessor activities must be completed. Project network models represent activities and milestones by arcs and nodes. PERT originally was an activity on arc network, in which the activities are represented on the lines and milestones on the nodes. Over time, some people began to use PERT as an activity on node network. For this discussion, we will use the original form of activity on arc.
PERT Chart

The milestones generally are numbered so that the ending node of an activity has a higher number than the beginning node. Incrementing the numbers by 10 allows for new ones to be inserted without modifying the numbering of the entire diagram. The activities in the above diagram are labeled with letters along with the expected time required to complete the activity.
Steps in the PERT Planning Process
PERT planning involves the following steps:
Identify the specific activities and milestones.
Determine the proper sequence of the activities.
Construct a network diagram.
Estimate the time required for each activity.
Determine the critical path.
Update the PERT chart as the project progresses.
1. Identify Activities and Milestones
The activities are the tasks required to complete the project. The milestones are the events marking the beginning and end of one or more activities. It is helpful to list the tasks in a table that in later steps can be expanded to include information on sequence and duration.
2. Determine Activity Sequence
This step may be combined with the activity identification step since the activity sequence is evident for some tasks. Other tasks may require more analysis to determine the exact order in which they must be performed.
3. Construct the Network Diagram
Using the activity sequence information, a network diagram can be drawn showing the sequence of the serial and parallel activities. For the original activity-on-arc model, the activities are depicted by arrowed lines and milestones are depicted by circles or "bubbles".
If done manually, several drafts may be required to correctly portray the relationships among activities. Software packages simplify this step by automatically converting tabular activity information into a network diagram.
4. Estimate Activity Times
Weeks are a commonly used unit of time for activity completion, but any consistent unit of time can be used.
A distinguishing feature of PERT is it's ability to deal with uncertainty in activity completion times. For each activity, the model usually includes three time estimates:
- Optimistic time - generally the shortest time in which the activity can be completed. It is common practice to specify optimistic times to be three standard deviations from the mean so that there is approximately a 1% chance that the activity will be completed within the optimistic time.
- Most likely time - the completion time having the highest probability. Note that this time is different from the expected time.
- Pessimistic time - the longest time that an activity might require. Three standard deviations from the mean is commonly used for the pessimistic time.
PERT assumes a beta probability distribution for the time estimates. For a beta distribution, the expected time for each activity can be approximated using the following weighted average:
Expected time = ( Optimistic + 4 x Most likely + Pessimistic ) / 6
This expected time may be displayed on the network diagram.
To calculate the variance for each activity completion time, if three standard deviation times were selected for the optimistic and pessimistic times, then there are six standard deviations between them, so the variance is given by:
[ ( Pessimistic - Optimistic ) / 6 ]2
5. Determine the Critical Path
The critical path is determined by adding the times for the activities in each sequence and determining the longest path in the project. The critical path determines the total calendar time required for the project. If activities outside the critical path speed up or slow down (within limits), the total project time does not change. The amount of time that a non-critical path activity can be delayed without delaying the project is referred to as slack time.
If the critical path is not immediately obvious, it may be helpful to determine the following four quantities for each activity:
ES - Earliest Start time
EF - Earliest Finish time
LS - Latest Start time
LF - Latest Finish time
These times are calculated using the expected time for the relevant activities. The earliest start and finish times of each activity are determined by working forward through the network and determining the earliest time at which an activity can start and finish considering its predecessor activities. The latest start and finish times are the latest times that an activity can start and finish without delaying the project. LS and LF are found by working backward through the network. The difference in the latest and earliest finish of each activity is that activity's slack. The critical path then is the path through the network in which none of the activities have slack.
The variance in the project completion time can be calculated by summing the variances in the completion times of the activities in the critical path. Given this variance, one can calculate the probability that the project will be completed by a certain date assuming a normal probability distribution for the critical path. The normal distribution assumption holds if the number of activities in the path is large enough for the central limit theorem to be applied.
Since the critical path determines the completion date of the project, the project can be accelerated by adding the resources required to decrease the time for the activities in the critical path. Such a shortening of the project sometimes is referred to as project crashing.
6. Update as Project Progresses
Make adjustments in the PERT chart as the project progresses. As the project unfolds, the estimated times can be replaced with actual times. In cases where there are delays, additional resources may be needed to stay on schedule and the PERT chart may be modified to reflect the new situation.
Benefits of PERT
PERT is useful because it provides the following information:
· Expected project completion time.
· Probability of completion before a specified date.
· The critical path activities that directly impact the completion time.
· The activities that have slack time and that can lend resources to critical path activities.
· Activity start and end dates.
Limitations
The following are some of PERT's weaknesses:
· The activity time estimates are somewhat subjective and depend on judgement. In cases where there is little experience in performing an activity, the numbers may be only a guess. In other cases, if the person or group performing the activity estimates the time there may be bias in the estimate.
· Even if the activity times are well-estimated, PERT assumes a beta distribution for these time estimates, but the actual distribution may be different.
· Even if the beta distribution assumption holds, PERT assumes that the probability distribution of the project completion time is the same as the that of the critical path. Because other paths can become the critical path if their associated activities are delayed, PERT consistently underestimates the expected project completion time.
The underestimation of the project completion time due to alternate paths becoming critical is perhaps the most serious of these issues. To overcome this limitation, Monte Carlo simulations can be performed on the network to eliminate this optimistic bias in the expected project completion time.
OWB - some steps to remember
Make a copy of the map before you make any changes and rename the copy to end with _OLD, _ORIG anything that identifies your map. Important If you rename the original map you will have to go into the process flow and point it to the new map as this association doesn’t change because of a name change. By renaming the copy you don’t lose this association.
After you copy and paste any object you should save and exit the owb client. We have seen issues with maps getting corrupted if not exited after pasting.
After changes are complete, save and then deploy the map. Fix any errors or warnings given during deployment. You can ignore “VLD-1119: Unable to generate Multi-table Insert statement for some or all targets.” Warning
Test both map and process flow where that map is used for all changes, changes to a map, or sychronization issues can cause the process flow to error.
Table changes neeed to be done carefully and the impact tool needs to be used to determine where that table is used. Each place that table is used you must go into that map and synchronize the table, this updates the changes to the map. not doing this step causes errors when map is run. Some changes will require more than just synchronization. You will see warnings during deployment if the column you updated requires more changes.
In General, make sure you check all places that an object is used when you make any change.
When you delete an object, make sure you uncheck the move to recycle bin option on the delete confirmation dialog box. This leaves a link between the deleted objects and the objects that it’s used in. This link causes mdl sizes to grow.
Before you export the mdl, Delete the copy you made when you started the changes, this deletes any links to that map and keeps the mdl size down.
Informatica Question Answers
1.While importing the relational source defintion from database,what are the meta data of source U import?
Source name
Database location
Column names
Datatypes
Key constraints
2. Howmany ways U can update a relational source defintion and what r they?
Two ways
1. Edit the definition
2. Reimport the defintion
3.Where should U place the flat file to import the flat file defintion to the designer?
Place it in local folder
4. To provide support for Mailframes source data,which files r used as a source definitions?
COBOL files
5. Which transformation should u need while using the cobol sources as source defintions?
Normalizer transformaiton which is used to normalize the data.Since cobol sources r oftenly consists of
Denaormailzed data.
6. How can U create or import flat file definition in to the warehouse designer?
U can not create or import flat file defintion in to warehouse designer directly.Instead U must analyze the file in source analyzer,then drag it into the warehouse designer.When U drag the flat file sorce defintion into warehouse desginer workspace,the warehouse designer creates a relational target defintion not a file defintion.If u want to load to a file,configure the session to write to a flat file.When the informatica server runs the session,it creates and loads the flatfile.
7.What is the maplet?
Maplet is a set of transformations that you build in the maplet designer and U can use in multiple mapings.
8. what is a transforamation?
It is a repostitory object that generates,modifies or passes data.
9. What r the dsigner tools for creating tranformations?
Mapping designer
Tansforamtion developer
Mapplet designer
10. What r the active and passive transforamtions?
An active transforamtion can change the number of rows that pass through it.A passive transformation does not change the number of rows that pass through it.
11. What r the connected or unconnected transforamations?
An unconnected transforamtion is not connected to other transformations in the mapping.Connected transforamation is connected to other transforamtions in the mapping.
12. How many ways u create ports?
Two ways
1.Drag the port from another transforamtion
2.Click the add buttion on the ports tab.
14. What r the reusable transforamtions?
Reusable transformations can be used in multiple mappings.When u need to incorporate this transformation into maping,U add an instance of it to maping.Later if U change the definition of the transformation ,all instances of it inherit the changes.Since the instance of reusable transforamation is a pointer to that transforamtion,U can change the transforamation in the transformation developer,its instances automatically reflect these changes.This feature can save U great deal of work.
15. What r the methods for creating reusable transforamtions?
Two methods
1.Design it in the transformation developer.
2.Promote a standard transformation from the mapping designer.After U add a transformation to the mapping , U can promote it to the status of reusable transformation.
Once U promote a standard transformation to reusable status,U can demote it to a standard transformation at any time.
If u change the properties of a reusable transformation in mapping,U can revert it to the original reusable transformation properties by clicking the revert button.
16.What r the unsupported repository objects for a mapplet?
COBOL source definition
Joiner transformations
Normalizer transformations
Non reusable sequence generator transformations.
Pre or post session stored procedures
Target defintions
Power mart 3.5 style Look Up functions
XML source definitions
IBM MQ source defintions
17. What r the mapping paramaters and maping variables?
Maping parameter represents a constant value that U can define before running a session.A mapping parameter retains the same value throughout the entire session.
When u use the maping parameter ,U declare and use the parameter in a maping or maplet.Then define the value of parameter in a parameter file for the session.
Unlike a mapping parameter,a maping variable represents a value that can change throughout the session.The informatica server saves the value of maping variable to the repository at the end of session run and uses that value next time U run the session.
18. Can U use the maping parameters or variables created in one maping into another maping?
NO.
We can use mapping parameters or variables in any transformation of the same maping or mapplet in which U have created maping parameters or variables.
19.Can u use the maping parameters or variables created in one maping into any other reusable transformation?
Yes.Because reusable tranformation is not contained with any maplet or maping.
20.How can U improve session performance in aggregator transformation?
Use sorted input.
21.What is aggregate cache in aggregator transforamtion?
The aggregator stores data in the aggregate cache until it completes aggregate calculations.When u run a session that uses an aggregator transformation,the informatica server creates index and data caches in memory to process the transformation.If the informatica server requires more space,it stores overflow values in cache files.
22.What r the diffrence between joiner transformation and source qualifier transformation?
U can join hetrogenious data sources in joiner transformation which we can not achieve in source qualifier transformation.
U need matching keys to join two relational sources in source qualifier transformation.Where as u doesn't need matching keys to join two sources.
Two relational sources should come from same datasource in sourcequalifier.U can join relatinal sources which r coming from diffrent sources also.
23.In which condtions we can not use joiner transformation(Limitaions of joiner transformation)?
Both pipelines begin with the same original data source.
Both input pipelines originate from the same Source Qualifier transformation.
Both input pipelines originate from the same Normalizer transformation.
Both input pipelines originate from the same Joiner transformation.
Either input pipelines contains an Update Strategy transformation.
Either input pipelines contains a connected or unconnected Sequence Generator transformation.
24.what r the settiing that u use to cofigure the joiner transformation?
Master and detail source
Type of join
Condition of the join
25. What r the join types in joiner transformation?
Normal (Default)
Master outer
Detail outer
Full outer
26.What r the joiner caches?
When a Joiner transformation occurs in a session, the Informatica Server reads all the records from the master source and builds index and data caches based on the master rows.
After building the caches, the Joiner transformation reads records from the detail source and
perform joins.
27.what is the look up transformation?
Use lookup transformation in u'r mapping to lookup data in a relational table,view,synonym.
Informatica server queries the look up table based on the lookup ports in the transformation.It compares the lookup transformation port values to lookup table column values based on the look up condition.
28.Why use the lookup transformation ?
To perform the following tasks.
Get a related value. For example, if your source table includes employee ID, but you want to include the employee name in your target table to make your summary data easier to read.
Perform a calculation. Many normalized tables include values used in a calculation, such as gross sales per invoice or sales tax, but not the calculated value (such as net sales).
Update slowly changing dimension tables. You can use a Lookup transformation to determine whether records already exist in the target.
29.What r the types of lookup?
Connected and unconnected
30.Differences between connected and unconnected lookup?
Connected lookup Unconnected lookup
Receives input values diectly from Receives input values from the result of a
the pipe line. lkp expression in a another transformation.
U can use a dynamic or static cache U can use a static cache.
Cache includes all lookup columns Cache includes all lookup out put ports in the
used in the maping lookup condition and the lookup/return port.
Support user defined default values Does not support user defiend default values
31.what is meant by lookup caches?
The informatica server builds a cache in memory when it processes the first row af a data in a cached look up transformation.It allocates memory for the cache based on the amount u configure in the transformation or session properties.The informatica server stores condition values in the index cache and output values in the data cache.
32.What r the types of lookup caches?
Persistent cache: U can save the lookup cache files and reuse them the next time the informatica server processes a lookup transformation configured to use the cache.
Recache from database: If the persistent cache is not synchronized with he lookup table,U can configure the lookup transformation to rebuild the lookup cache.
Static cache: U can configure a static or readonly cache for only lookup table.By default informatica server creates a static cache.It caches the lookup table and lookup values in the cache for each row that comes into the transformation.when the lookup condition is true,the informatica server does not update the cache while it prosesses the lookup transformation.
Dynamic cache: If u want to cache the target table and insert new rows into cache and the target,u can create a look up transformation to use dynamic cache.The informatica server dynamically inerts data to the target table.
shared cache: U can share the lookup cache between multiple transactions.U can share unnamed cache between transformations inthe same maping.
33. Difference between static cache and dynamic cache
Static cache Dynamic cache
U can not inert or update the cache. U can insert rows into the cache as u pass
to the target
The informatic server returns a value from The informatic server inserts rows into cache
the lookup table opr cache when the condition when the condition is false.This indicates that
is true.When the condition is not true,the the row is not in the cache or target table.
informatica server returns the default value U can pass these rows to the target table.
for connected transformations and null for
unconnected transformations.
34.Which transformation should we use to normalize the COBOL and relational sources?
Normalizer Transformation.
When U drag the COBOL source in to the mapping Designer workspace,the normalizer transformation automatically appears,creating input and output ports for every column in the source.
35.How the informatica server sorts the string values in Ranktransformation?
When the informatica server runs in the ASCII data movement mode it sorts session data using Binary sortorder.If U configure the seeion to use a binary sort order,the informatica server caluculates the binary value of each string and returns the specified number of rows with the higest binary values for the string.
36.What r the rank caches?
During the session ,the informatica server compares an inout row with rows in the datacache.If the input row out-ranks a stored row,the informatica server replaces the stored row with the input row.The informatica server stores group information in an index cache and row data in a data cache.
37.What is the Rankindex in Ranktransformation?
The Designer automatically creates a RANKINDEX port for each Rank transformation. The Informatica Server uses the Rank Index port to store the ranking position for each record in a group. For example, if you create a Rank transformation that ranks the top 5 salespersons for each quarter, the rank index numbers the salespeople from 1 to 5:
38.What is the Router transformation?
A Router transformation is similar to a Filter transformation because both transformations allow you to use a condition to test data. However, a Filter transformation tests data for one condition and drops the rows of data that do not meet the condition. A Router transformation tests data for one or more conditions and gives you the option to route rows of data that do not meet any of the conditions to a default output group.
If you need to test the same input data based on multiple conditions, use a Router Transformation in a mapping instead of creating multiple Filter transformations to perform the same task.
39.What r the types of groups in Router transformation?
Input group
Output group
The designer copies property information from the input ports of the input group to create a set of output ports for each output group.
Two types of output groups
User defined groups
Default group
U can not modify or delete default groups.
40.Why we use stored procedure transformation?
For populating and maintaining data bases.
42.What r the types of data that passes between informatica server and stored procedure?
3 types of data
Input/Out put parameters
Return Values
Status code.
43.What is the status code?
Status code provides error handling for the informatica server during the session.The stored procedure issues a status code that notifies whether or not stored procedure completed sucessfully.This value can not seen by the user.It only used by the informatica server to determine whether to continue running the session or stop.
44. What is source qualifier transformation?
When U add a relational or a flat file source definition to a maping,U need to connect it to
a source qualifer transformation.The source qualifier transformation represnets the records
that the informatica server reads when it runs a session.
45.What r the tasks that source qualifier performs?
Join data originating from same source data base.
Filter records when the informatica server reads source data.
Specify an outer join rather than the default inner join
specify sorted records.
Select only distinct values from the source.
Creating custom query to issue a special SELECT statement for the informatica server to read
source data.
46. What is the target load order?
U specify the target loadorder based on source qualifiers in a maping.If u have the multiple
source qualifiers connected to the multiple targets,U can designatethe order in which informatica
server loads data into the targets.
47.What is the default join that source qualifier provides?
Inner equi join.
48. What r the basic needs to join two sources in a source qualifier?
Two sources should have primary and Foreign key relation ships.
Two sources should have matching data types.
49.what is update strategy transformation ?
This transformation is used to maintain the history data or just most recent changes in to target
table.
50.Describe two levels in which update strategy transformation sets?
Within a session. When you configure a session, you can instruct the Informatica Server to either treat all records in the same way (for example, treat all records as inserts), or use instructions coded into the session mapping to flag records for different database operations.
Within a mapping. Within a mapping, you use the Update Strategy transformation to flag records for insert, delete, update, or reject.
51.What is the default source option for update stratgey transformation?
Data driven.
52. What is Datadriven?
The informatica server follows instructions coded into update strategy transformations with
in the session maping determine how to flag records for insert,update,,delete or reject
If u do not choose data driven option setting,the informatica server ignores all update strategy
transformations in the mapping.
53.What r the options in the target session of update strategy transsformatioin?
Insert
Delete
Update
Update as update
Update as insert
Update esle insert
Truncate table
54. What r the types of maping wizards that r to be provided in Informatica?
The Designer provides two mapping wizards to help you create mappings quickly and easily. Both wizards are designed to create mappings for loading and maintaining star schemas, a series of dimensions related to a central fact table.
Getting Started Wizard. Creates mappings to load static fact and dimension tables, as well as slowly growing dimension tables.
Slowly Changing Dimensions Wizard. Creates mappings to load slowly changing dimension tables based on the amount of historical dimension data you want to keep and the method you choose to handle historical dimension data.
55. What r the types of maping in Getting Started Wizard?
Simple Pass through maping :
Loads a static fact or dimension table by inserting all rows. Use this mapping when you want to drop all existing data from your table before loading new data.
Slowly Growing target :
Loads a slowly growing fact or dimension table by inserting new rows. Use this mapping to load new data when existing data does not require updates.
56. What r the mapings that we use for slowly changing dimension table?
Type1: Rows containing changes to existing dimensions are updated in the target by overwriting the existing dimension. In the Type 1 Dimension mapping, all rows contain current dimension data.
Use the Type 1 Dimension mapping to update a slowly changing dimension table when you do not need to keep any previous versions of dimensions in the table.
Type 2: The Type 2 Dimension Data mapping inserts both new and changed dimensions into the target. Changes are tracked in the target table by versioning the primary key and creating a version number for each dimension in the table.
Use the Type 2 Dimension/Version Data mapping to update a slowly changing dimension table when you want to keep a full history of dimension data in the table. Version numbers and versioned primary keys track the order of changes to each dimension.
Type 3: The Type 3 Dimension mapping filters source rows based on user-defined comparisons and inserts only those found to be new dimensions to the target. Rows containing changes to existing dimensions are updated in the target. When updating an existing dimension, the Informatica Server saves existing data in different columns of the same row and replaces the existing data with the updates
57.What r the different types of Type2 dimension maping?
Type2 Dimension/Version Data Maping: In this maping the updated dimension in the source will gets inserted in target along with a new version number.And newly added dimension
in source will inserted into target with a primary key.
Type2 Dimension/Flag current Maping: This maping is also used for slowly changing dimensions.In addition it creates a flag value for changed or new dimension.
Flag indiactes the dimension is new or newlyupdated.Recent dimensions will gets saved with cuurent flag value 1. And updated dimensions r saved with the value 0.
Type2 Dimension/Effective Date Range Maping: This is also one flavour of Type2 maping used for slowly changing dimensions.This maping also inserts both new and changed dimensions in to the target.And changes r tracked by the effective date range for each version of each dimension.
58.How can u recognise whether or not the newly added rows in the source r gets insert in the target ?
In the Type2 maping we have three options to recognise the newly added rows
Version number
Flagvalue
Effective date Range
59. What r two types of processes that informatica runs the session?
Load manager Process: Starts the session, creates the DTM process, and sends post-session email when the session completes.
The DTM process. Creates threads to initialize the session, read, write, and transform data, and handle pre- and post-session operations.
60. What r the new features of the server manager in the informatica 5.0?
U can use command line arguments for a session or batch.This allows U to change the values of session parameters,and mapping parameters and maping variables.
Parallel data processig: This feature is available for powercenter only.If we use the informatica server on a SMP system,U can use multiple CPU's to process a session concurently.
Process session data using threads: Informatica server runs the session in two processes.Explained in previous question.
61. Can u generate reports in Informatcia?
Yes. By using Metadata reporter we can generate reports in informatica.
62.What is metadata reporter?
It is a web based application that enables you to run reports againist repository metadata.
With a meta data reporter,u can access information about U'r repository with out having knowledge of sql,transformation language or underlying tables in the repository.
63.Define maping and sessions?
Maping: It is a set of source and target definitions linked by transformation objects that define the rules for transformation.
Session : It is a set of instructions that describe how and when to move data from source to targets.
64.Which tool U use to create and manage sessions and batches and to monitor and stop the informatica server?
Informatica server manager.
65.Why we use partitioning the session in informatica?
Partitioning achieves the session performance by reducing the time period of reading the source and loading the data into ta
es multiple connections to the target and loads partitions of data concurently.
For XML and file sources,informatica server reads multiple files concurently.For loading the data informatica server creates a seperate file for each partition(of a source file).U can choose to merge the targets.
68. Why u use repository connectivity?
When u edit,schedule the sesion each time,informatica server directly communicates the repository to check whether or not the session and users r valid.All the metadata of sessions and mappings will be stored in repository.
69.What r the tasks that Loadmanger process will do?
Manages the session and batch scheduling: Whe u start the informatica server the load maneger launches and queries the repository for a list of sessions configured to run on the informatica server.When u configure the session the loadmanager maintains list of list of sessions and session start times.When u sart a session loadmanger fetches the session information from the repository to perform the validations and verifications prior to starting DTM process.
Locking and reading the session: When the informatica server starts a session lodamaager locks the session from the repository.Locking prevents U starting the session again and again.
Reading the parameter file: If the session uses a parameter files,loadmanager reads the parameter file and verifies that the session level parematers are declared in the file
Verifies permission and privelleges: When the sesson starts load manger checks whether or not the user have privelleges to run the session.
Creating log files: Loadmanger creates logfile contains the status of session.
70. What is DTM process?
After the loadmanger performs validations for session,it creates the DTM process.DTM is to create and manage the threads that carry out the session tasks.I creates the master thread.Master thread creates and manges all the other threads.
71. What r the different threads in DTM process?
Master thread: Creates and manages all other threads
Maping thread: One maping thread will be creates for each session.Fectchs session and maping information.
Pre and post session threads: This will be created to perform pre and post session operations.
Reader thread: One thread will be created for each partition of a source.It reads data from source.
Writer thread: It will be created to load data to the target.
Transformation thread: It will be created to tranform data.
72.What r the data movement modes in informatcia?
Datamovement modes determines how informatcia server handles the charector data.U choose the datamovement in the informatica server configuration settings.Two types of datamovement modes avialable in informatica.
ASCII mode
Uni code mode.
73. What r the out put files that the informatica server creates during the session running?
Informatica server log: Informatica server(on unix) creates a log for all status and error messages(default name: pm.server.log).It also creates an error log for error messages.These files will be created in informatica home directory.
Session log file: Informatica server creates session log file for each session.It writes information about session into log files such as initialization process,creation of sql commands for reader and writer threads,errors encountered and load summary.The amount of detail in session log file depends on the tracing level that u set.
Session detail file: This file contains load statistics for each targets in mapping.Session detail include information such as table name,number of rows written or rejected.U can view this file by double clicking on the session in monitor window
Performance detail file: This file contains information known as session performance details which helps U where performance can be improved.To genarate this file select the performance detail option in the session property sheet.
Reject file: This file contains the rows of data that the writer does notwrite to targets.
Control file: Informatica server creates control file and a target file when U run a session that uses the external loader.The control file contains the information about the target flat file such as data format and loading instructios for the external loader.
Post session email: Post session email allows U to automatically communicate information about a session run to designated recipents.U can create two different messages.One if the session completed sucessfully the other if the session fails.
Indicator file: If u use the flat file as a target,U can configure the informatica server to create indicator file.For each target row,the indicator file contains a number to indicate whether the row was marked for insert,update,delete or reject.
output file: If session writes to a target file,the informatica server creates the target file based on file prpoerties entered in the session property sheet.
Cache files: When the informatica server creates memory cache it also creates cache files.For the following circumstances informatica server creates index and datacache files.
Aggreagtor transformation
Joiner transformation
Rank transformation
Lookup transformation
74.In which circumstances that informatica server creates Reject files?
When it encounters the DD_Reject in update strategy transformation.
Violates database constraint
Filed in the rows was truncated or overflowed.
75. What is polling?
It displays the updated information about the session in the monitor window.The monitor window displays the status of each session when U poll the informatica server
76. Can u copy the session to a different folder or repository?
Yes. By using copy session wizard u can copy a session in a different folder or repository.But that target folder or repository should consists of mapping of that session.If target folder or repository is not having the maping of copying session , u should have to copy that maping first before u copy the session.
77. What is batch and describe about types of batches?
Grouping of session is known as batch.Batches r two types
Sequential: Runs sessions one after the other
Concurrent: Runs session at same time.
If u have sessions with source-target dependencies u have to go for sequential batch to start the sessions one after another.If u have several independent sessions u can use concurrent batches.Whcih runs all the sessions at the same time.
78. Can u copy the batches?
NO
79.How many number of sessions that u can create in a batch?
Any number of sessions.
80.When the informatica server marks that a batch is failed?
If one of session is configured to "run if previous completes" and that previous session fails.
81. What is a command that used to run a batch?
pmcmd is used to start a batch.
82. What r the different options used to configure the sequential batches?
Two options
Run the session only if previous session completes sucessfully.
Always runs the session.
83. In a sequential batch can u run the session if previous session fails?
Yes.By setting the option always runs the session.
84. Can u start a batches with in a batch?
U can not. If u want to start batch that resides in a batch,create a new independent batch and copy the necessary sessions into the new batch.
85. Can u start a session inside a batch idividually?
We can start our required session only in case of sequential batch.in case of concurrent batch
we cant do like this.
86. How can u stop a batch?
By using server manager or pmcmd.
87. What r the session parameters?
Session parameters r like maping parameters,represent values U might want to change between
sessions such as database connections or source files.
Server manager also allows U to create userdefined session parameters.Following r user defined
session parameters.
Database connections
Source file names: use this parameter when u want to change the name or location of
session source file between session runs
Target file name : Use this parameter when u want to change the name or location of
session target file between session runs.
Reject file name : Use this parameter when u want to change the name or location of
session reject files between session runs.
88. What is parameter file?
Parameter file is to define the values for parameters and variables used in a session.A parameter
file is a file created by text editor such as word pad or notepad.
U can define the following values in parameter file
Maping parameters
Maping variables
session parameters
89. How can u access the remote source into U'r session?
Relational source: To acess relational source which is situated in a remote place ,u need to
configure database connection to the datasource.
FileSource : To access the remote source file U must configure the FTP connection to the
host machine before u create the session.
Hetrogenous : When U'r maping contains more than one source type,the server manager creates
a hetrogenous session that displays source options for all types.
90. What is difference between partioning of relatonal target and partitioning of file targets?
If u parttion a session with a relational target informatica server creates multiple connections
to the target database to write target data concurently.If u partition a session with a file target
the informatica server creates one target file for each partition.U can configure session properties
to merge these target files.
91. what r the transformations that restricts the partitioning of sessions?
Advanced External procedure tranformation and External procedure transformation: This
transformation contains a check box on the properties tab to allow partitioning.
Aggregator Transformation: If u use sorted ports u can not parttion the assosiated source
Joiner Transformation : U can not partition the master source for a joiner transformation
Normalizer Transformation
XML targets.
92. Performance tuning in Informatica?
The goal of performance tuning is optimize session performance so sessions run during the available load window for the Informatica Server.Increase the session performance by following.
The performance of the Informatica Server is related to network connections. Data generally moves across a network at less than 1 MB per second, whereas a local disk moves data five to twenty times faster. Thus network connections ofteny affect on session performance.So aviod
netwrok connections.
Flat files: If u'r flat files stored on a machine other than the informatca server, move those files to the machine that consists of informatica server.
Relational datasources: Minimize the connections to sources ,targets and informatica server to
improve session performance.Moving target database into server system may improve session
performance.
Staging areas: If u use staging areas u force informatica server to perform multiple datapasses.
Removing of staging areas may improve session performance.
U can run the multiple informatica servers againist the same repository.Distibuting the session load to multiple informatica servers may improve session performance.
Run the informatica server in ASCII datamovement mode improves the session performance.Because ASCII datamovement mode stores a character value in one byte.Unicode mode takes 2 bytes to store a character.
If a session joins multiple source tables in one Source Qualifier, optimizing the query may improve performance. Also, single table select statements with an ORDER BY or GROUP BY clause may benefit from optimization such as adding indexes.
We can improve the session performance by configuring the network packet size,which allows
data to cross the network at one time.To do this go to server manger ,choose server configure database connections.
If u r target consists key constraints and indexes u slow the loading of data.To improve the session performance in this case drop constraints and indexes before u run the session and rebuild them after completion of session.
Running a parallel sessions by using concurrent batches will also reduce the time of loading the
data.So concurent batches may also increase the session performance.
Partittionig the session improves the session performance by creating multiple connections to sources and targets and loads data in paralel pipe lines.
In some cases if a session contains a aggregator transformation ,u can use incremental aggregation to improve session performance.
Aviod transformation errors to improve the session performance.
If the sessioin containd lookup transformation u can improve the session performance by enabling the look up cache.
If U'r session contains filter transformation ,create that filter transformation nearer to the sources
or u can use filter condition in source qualifier.
Aggreagator,Rank and joiner transformation may oftenly decrease the session performance .Because they must group data before processing it.To improve session performance in this case use sorted ports option.
92. What is difference between maplet and reusable transformation?
Maplet consists of set of transformations that is reusable.A reusable transformation is a single transformation that can be reusable.
If u create a variables or parameters in maplet that can not be used in another maping or maplet.Unlike the variables that r created in a reusable transformation can be usefull in any other maping or maplet.
We can not include source definitions in reusable transformations.But we can add sources to a maplet.
Whole transformation logic will be hided in case of maplet.But it is transparent in case of reusable transformation.
We cant use COBOL source qualifier,joiner,normalizer transformations in maplet.Where as we can make them as a reusable transformations.
93. Define informatica repository?
The Informatica repository is a relational database that stores information, or metadata, used by the Informatica Server and Client tools. Metadata can include information such as mappings describing how to transform source data, sessions indicating when you want the Informatica Server to perform the transformations, and connect strings for sources and targets.
The repository also stores administrative information such as usernames and passwords, permissions and privileges, and product version.
Use repository manager to create the repository.The Repository Manager connects to the repository database and runs the code needed to create the repository tables.Thsea tables
stores metadata in specific format the informatica server,client tools use.
94. What r the types of metadata that stores in repository?
Following r the types of metadata that stores in the repository
Database connections
Global objects
Mappings
Mapplets
Multidimensional metadata
Reusable transformations
Sessions and batches
Short cuts
Source definitions
Target defintions
Transformations
95. What is power center repository?
The PowerCenter repository allows you to share metadata across repositories to create a data mart domain. In a data mart domain, you can create a single global repository to store metadata used across an enterprise, and a number of local repositories to share the global metadata as needed.
96. How can u work with remote database in informatica?did u work directly by using remote
connections?
To work with remote datasource u need to connect it with remote connections.But it is not
preferable to work with that remote source directly by using remote connections .Instead u bring that source into U r local machine where informatica server resides.If u work directly with remote source the session performance will decreases by passing less amount of data across the network in a particular time.
97. What r the new features in Informatica 5.0?
U can Debug U'r maping in maping designer
U can view the work space over the entire screen
The designer displays a new icon for a invalid mapings in the navigator window
U can use a dynamic lookup cache in a lokup transformation
Create maping parameters or maping variables in a maping or maplet to make mapings more
flexible
U can export objects into repository and import objects from repository.when u export a repository object,the designer or server manager creates an XML file to describe the repository metadata.
The designer allows u to use Router transformation to test data for multiple conditions.Router transformation allows u route groups of data to transformation or target.
U can use XML data as a source or target.
Server Enahancements:
U can use the command line program pmcmd to specify a parameter file to run sessions or batches.This allows you to change the values of session parameters, and mapping parameters and variables at runtime.
If you run the Informatica Server on a symmetric multi-processing system, you can use multiple CPUs to process a session concurrently. You configure partitions in the session properties based on source qualifiers. The Informatica Server reads, transforms, and writes partitions of data in parallel for a single session. This is avialable for Power center only.
Informatica server creates two processes like loadmanager process,DTM process to run the sessions.
Metadata Reporter: It is a web based application which is used to run reports againist repository metadata.
U can copy the session across the folders and reposotories using the copy session wizard in the informatica server manager
With new email variables, you can configure post-session email to include information, such as the mapping used during the session
98. what is incremantal aggregation?
When using incremental aggregation, you apply captured changes in the source to aggregate calculations in a session. If the source changes only incrementally and you can capture changes, you can configure the session to process only those changes. This allows the Informatica Server to update your target incrementally, rather than forcing it to process the entire source and recalculate the same calculations each time you run the session.
99. What r the scheduling options to run a sesion?
U can shedule a session to run at a given time or intervel,or u can manually run the session.
Different options of scheduling
Run only on demand: Informatica server runs the session only when user starts session explicitly
Run once: Informatica server runs the session only once at a specified date and time.
Run every: Informatica server runs the session at regular intervels as u configured.
Customized repeat: Informatica server runs the session at the dats and times secified in the repeat dialog box.
100 .What is tracing level and what r the types of tracing level?
Tracing level represents the amount of information that informatcia server writes in a log file.
Types of tracing level
Normal
Verbose
Verbose init
Verbose data
101. What is difference between stored procedure transformation and external procedure transformation?
In case of storedprocedure transformation procedure will be compiled and executed in a relational data source.U need data base connection to import the stored procedure in to u'r maping.Where as in external procedure transformation procedure or function will be executed out side of data source.Ie u need to make it as a DLL to access in u r maping.No need to have data base connection in case of external procedure transformation.
102. Explain about Recovering sessions?
If you stop a session or if an error causes a session to stop, refer to the session and error logs to determine the cause of failure. Correct the errors, and then complete the session. The method you use to complete the session depends on the properties of the mapping, session, and Informatica Server configuration.
Use one of the following methods to complete the session:
· Run the session again if the Informatica Server has not issued a commit.
· Truncate the target tables and run the session again if the session is not recoverable.
· Consider performing recovery if the Informatica Server has issued at least one commit.
103. If a session fails after loading of 10,000 records in to the target.How can u load the records from 10001 th record when u run the session next time?
As explained above informatcia server has 3 methods to recovering the sessions.Use performing recovery to load the records from where the session fails.
104. Explain about perform recovery?
When the Informatica Server starts a recovery session, it reads the OPB_SRVR_RECOVERY table and notes the row ID of the last row committed to the target database. The Informatica Server then reads all sources again and starts processing from the next row ID. For example, if the Informatica Server commits 10,000 rows before the session fails, when you run recovery, the Informatica Server bypasses the rows up to 10,000 and starts loading with row 10,001.
By default, Perform Recovery is disabled in the Informatica Server setup. You must enable Recovery in the Informatica Server setup before you run a session so the Informatica Server can create and/or write entries in the OPB_SRVR_RECOVERY table.
105. How to recover the standalone session?
A standalone session is a session that is not nested in a batch. If a standalone session fails, you can run recovery using a menu command or pmcmd. These options are not available for batched sessions.
To recover sessions using the menu:
1. In the Server Manager, highlight the session you want to recover.
2. Select Server Requests-Stop from the menu.
3. With the failed session highlighted, select Server Requests-Start Session in Recovery Mode from the menu.
To recover sessions using pmcmd:
1.From the command line, stop the session.
2. From the command line, start recovery.
106. How can u recover the session in sequential batches?
If you configure a session in a sequential batch to stop on failure, you can run recovery starting with the failed session. The Informatica Server completes the session and then runs the rest of the batch. Use the Perform Recovery session property
To recover sessions in sequential batches configured to stop on failure:
1.In the Server Manager, open the session property sheet.
2.On the Log Files tab, select Perform Recovery, and click OK.
3.Run the session.
4.After the batch completes, open the session property sheet.
5.Clear Perform Recovery, and click OK.
If you do not clear Perform Recovery, the next time you run the session, the Informatica Server attempts to recover the previous session.
If you do not configure a session in a sequential batch to stop on failure, and the remaining sessions in the batch complete, recover the failed session as a standalone session.
107. How to recover sessions in concurrent batches?
If multiple sessions in a concurrent batch fail, you might want to truncate all targets and run the batch again. However, if a session in a concurrent batch fails and the rest of the sessions complete successfully, you can recover the session as a standalone session.
To recover a session in a concurrent batch:
1.Copy the failed session using Operations-Copy Session.
2.Drag the copied session outside the batch to be a standalone session.
3.Follow the steps to recover a standalone session.
4.Delete the standalone copy.
108. How can u complete unrcoverable sessions?
Under certain circumstances, when a session does not complete, you need to truncate the target tables and run the session from the beginning. Run the session from the beginning when the Informatica Server cannot run recovery or when running recovery might result in inconsistent data.
109. What r the circumstances that infromatica server results an unreciverable session?
The source qualifier transformation does not use sorted ports.
If u change the partition information after the initial session fails.
Perform recovery is disabled in the informatica server configuration.
If the sources or targets changes after initial session fails.
If the maping consists of sequence generator or normalizer transformation.
If a concuurent batche contains multiple failed sessions.
110. If i done any modifications for my table in back end does it reflect in informatca warehouse or maping desginer or source analyzer?
NO. Informatica is not at all concern with back end data base.It displays u all the information
that is to be stored in repository.If want to reflect back end changes to informatica screens,
again u have to import from back end to informatica by valid connection.And u have to replace the existing files with imported files.



